Ranked #1 in Accurate and Reliable Estimation Services
A Fastest Turnaround 24 Hours!
Ranked #1 in Accurate and Reliable Estimation Services
A Fastest Turnaround 24 Hours!
Ranked #1 in Accurate and Reliable Estimation Services
A Fastest Turnaround 24 Hours!
Ranked #1 in Accurate and Reliable Estimation Services
A Fastest Turnaround 24 Hours!

For any construction project to succeed, precise estimation of labor costs is essential. It helps control the budget and minimizes financial shocks while ensuring fair payment to workers. Failure to adequately plan for construction projects tends to result in exorbitant expenses, especially about labor. Precise planning of the financial aspects of a construction project is integral to achieving the successful realization of the project. This guide is going to walk you through the process of calculating labor costs, helping you keep your project on solid financial ground through all its phases.
Labor costs in construction refer to the expenses associated with hiring workers for a project. These costs can be divided into several components:

Estimating labor costs requires a systematic approach that incorporates all components of the workforce spend. It is critical to capture each detail. To simplify every process, here is a guide to accurately calculating labor costs.
The first step is estimating how many workers are required for the project. Consider the site’s size, the tasks’ complexity, and the project’s timeline. For example:
Depending on the scale and complexity of the project, this number will change. Larger projects will require more workers and possibly specialized labor, like electricians or masons.
Once you’ve determined the number of workers needed, you must calculate the hourly wage for each worker. Rates can vary depending on the region, experience, and job type. Here are some example wages:
These wages can vary based on location and specific industry standards, but these numbers will serve as a guide for your estimation. It’s important to research the typical hourly rates for workers in your area or industry.
Labor burden refers to additional expenses beyond workers’ direct wages. These costs may include:
Labor burden is typically expressed as a percentage of the worker’s wages. For example, if the labor burden is 25%, you must multiply the worker’s hourly wage by 1.25 to account for these costs.
It’s crucial to remember that labor burden can vary significantly depending on the location, company size, and whether the worker is a full-time employee or subcontractor.
Next, you’ll need to estimate how many hours each worker will be on the job. Labor hours depend on the scope and schedule of the project. For example, if you’re planning a 3-day project with 8-hour workdays, the total number of hours for each worker would be:
Now, calculate the total labor hours for the project by summing up the hours for each worker.
Finally, calculate the total labor cost by multiplying the adjusted hourly rate (including labor burden) by the total hours worked for each worker.
Now, add up the costs for each worker:
Thus, the total labor cost for the 3-day project would be $2,130.
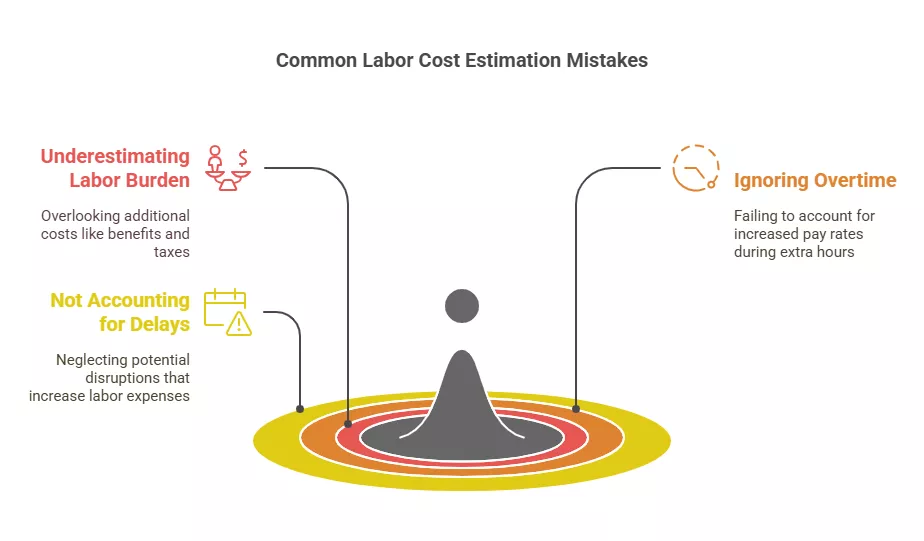
Estimating labor costs can be tricky, and mistakes can be costly. Here are some common pitfalls to watch out for:
Although often ignored during the estimation phase, the impact of labor burden could substantially inflate the cost of labor. Make sure to incorporate the entire labor burden so that your calculations don’t underestimate costs.
In the event that you have workers who are required to attend shifts that are considered overtime, ensure that you factor this into your relevant cost assessments. Overtime payment is usually 1.5 times more than the normal amount paid for each hour of work, greatly increasing your overall expenses on labor. If you project that overtime will be needed, remember to account for it in the highly preliminary planning stage of your budget.
Construction endeavors are seldom executed in accordance with the schedule. Weather changes, material unavailability, and other various complications often add to labor expenses. It is good practice to estimate delays and make necessary adjustments to labor costs. Making such estimates further reduces the possibility of surprises.
To streamline the process of estimating labor costs, you can use specialized software and tools. Here are a few popular options:
These tools can save you time and improve the accuracy of your labor cost estimates.
Effective labor cost estimation is necessary for effective scheduling and tracking of construction projects. Adhering to the instructions in this guide will ensure that estimates are optimized, aiding in positive cash flow projections and budgets during construction. Remember that labor burden, overtime to standard hours, and scheduling delays are significant factors and must be considered in calculations.
Consider using services such as Axis Estimation to improve accuracy in estimating labor costs. These professionals provide specialized and detailed estimates of construction labor costs and help clients avoid common pitfalls, thus staying within budget.
0 Comments