Ranked #1 in Accurate and Reliable Estimation Services
A Fastest Turnaround 24 Hours!
Ranked #1 in Accurate and Reliable Estimation Services
A Fastest Turnaround 24 Hours!
Ranked #1 in Accurate and Reliable Estimation Services
A Fastest Turnaround 24 Hours!
Ranked #1 in Accurate and Reliable Estimation Services
A Fastest Turnaround 24 Hours!

Productivity is defined as the ratio between output and input, and so, it is one of the most important assets or crippling weaknesses for any business. If it’s a construction site, a manufacturing assembly line, or a service based unit; knowing exactly how to evaluate labor productivity will help to optimize operations. But what can one do to check if their employees are at the top of their game? How do you measure.Workforce instrumentation? In this article, we will examine how to calculate and evaluate labor productivity, with practical recommendations on how to improve it cross-sector.
Labor productivity konomi is considered as the value generated when considered by a ratio of hours worked or labor applied (output). Increased productivity of labor yields additional output without increasing cost and translates into increased sophistication of construction industries.
They offer comparisons and surveys related to construction. Construction professionals and organizations actively partake in knowledge gathering and sharing through various digital solutions.
In industrial branches like-in design which is the final phase of assembly and aids in part ranges from-drawing mechanisms, technological analyses are offered. Navigation employs constructs sorted into definite sections enabling students to instantly reach and exercise in their field of study.
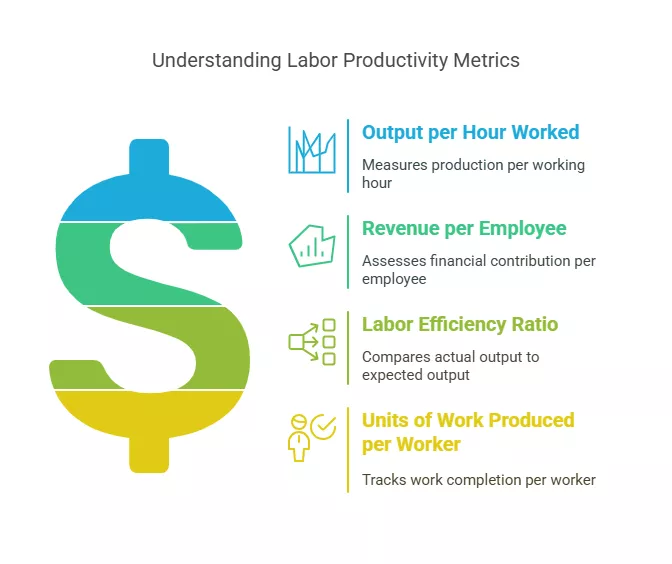
Measuring and estimating labor productivity is crucial for improving business efficiency and profitability. By using the right metrics and tools, businesses can gain valuable insights into workforce performance and identify areas for improvement. Whether you’re in construction, manufacturing, or services, understanding and optimizing labor productivity can help you stay competitive and achieve long-term success.
For more insights on construction estimation services, visit our website and stay updated on the latest trends and practices in labor cost estimation.
0 Comments